- L&D INSIGHTS/
- Top 25 Questions for 360 Feedback/


Top 25 Questions for 360 Feedback
- L&D INSIGHTS/
- Top 25 Questions for 360 Feedback/
Top 25 Questions for 360 Feedback
360-degree feedback is an employee evaluation approach that gathers information from various sources, including peers, direct reports, supervisors, and external stakeholders like customers or suppliers. The method often features a self-assessment by the individual, completing the “360” circle of perspectives. All these viewpoints are collected to provide a detailed picture of a person’s performance, strengths, and areas for improvement.
In this article, we will look at ways of writing effective questions for 360 feedback, how you can use them to assess core competencies and go over different tools and technologies that can help facilitate this process.
Open-Ended vs. Closed-Ended Questions For 360 Feedback
You will typically use both open-ended and closed-ended questions and need to understand the purpose of each distinctive type.
10 Open-Ended Questions
Open-ended questions excel at capturing qualitative insights, context, and examples. They are especially useful for evaluating soft skills or complex areas like leadership, teamwork, or problem-solving, where a rating alone may not tell the full story. Here are some examples to consider:
- What are this employee’s greatest strengths?
- In what areas could this employee improve?
- How effectively does this employee communicate with others?
- Can you provide an example of when this employee demonstrated leadership?
- Describe a situation where this employee went above and beyond their duties.
- How does this employee handle stress or pressure?
- How does this employee adapt to changes or unexpected challenges?
- What is one behaviour this employee should continue doing?
- What is one thing this employee could start doing to be more effective?
- How does this employee support the company’s values and culture?
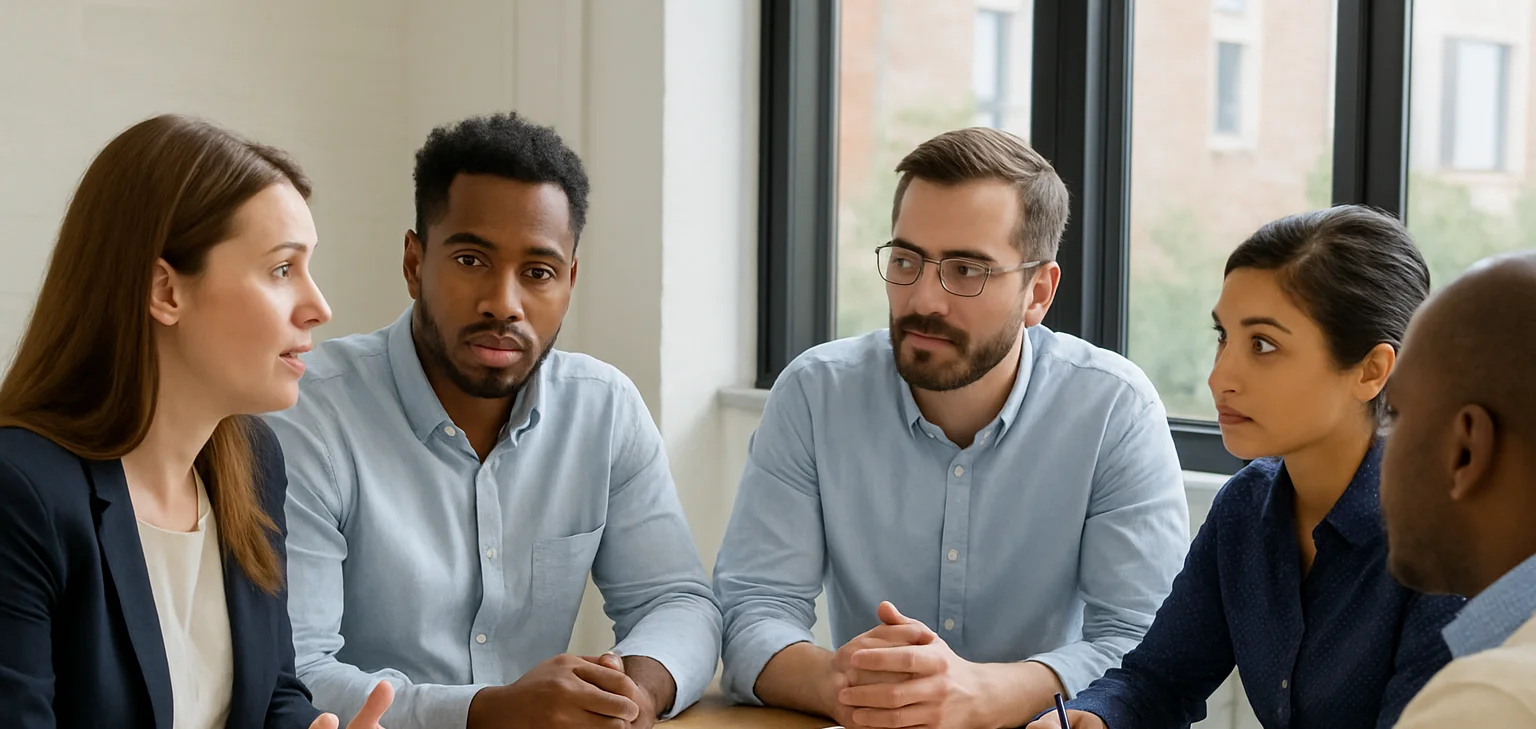
Download our Training Needs Analysis Form
 Download now
Download now10 Close-Ended Questions
A common format in 360 surveys is the Likert scale, where a respondent rates their level of agreement or frequency on a scale (e.g., 1 = Strongly Disagree up to 5 = Strongly Agree). Straightforward Yes/No questions for 360 feedback are also common. Here is a list of some popular options to choose from:
- Does this employee consistently meet deadlines?
- Is this employee a good team player?
- Does this employee take initiative without being asked?
- Is this employee dependable when it comes to their responsibilities?
- Does the employee demonstrate a positive attitude at work?
- Is this employee open to receiving feedback from others?
- Does this employee handle conflicts effectively?
- Is the employee knowledgeable in their field of work?
- Does the employee uphold high ethical standards?
- Is this employee proactive in solving problems?
- Essentially, this combination provides a robust feedback dataset that includes both numbers and narratives.
360 Feedback Questions for Managers and Leaders
When implementing 360-degree feedback, you need to consider who is being evaluated and tailor questions accordingly. For managers and senior leaders, 360 feedback questions the focus must be on leadership competencies – things like guiding the team, strategic thinking, decision-making, and mentoring others. Here are 5 sample questions to help you see the difference:
- In what ways does this leader inspire and motivate others?
- How well does this individual communicate their vision and goals to the team?
- How does this manager handle challenging situations or crises?
- To what extent does this leader provide clear and constructive feedback to their team?
- How well does this manager delegate tasks and responsibilities?
These questions focus on leadership behaviours and are phrased in ways that a subordinate or employee could observe. Together, they will provide you with a comprehensive view of a manager’s impact.
Are you thinking about boosting your team's IT skills?
Download our Quick IT Course Guide
 Download now
Download nowHow to Use 360 Feedback Questions to Assess Core Competencies
Most 360-degree feedback programs are built around assessing an employee on a set of core competencies. The most commonly examined skill domains include:
- Communication: This refers to how effectively an employee exchanges information – including clarity, listening, adapting to audiences, and overall interpersonal communication skills.
- Problem-Solving: It covers an employee’s ability to analyse issues, find solutions, make decisions, and overcome challenges. It’s crucial for roles that involve critical thinking or troubleshooting.
- Leadership: The leadership competency encompasses how the individual influences and guides others towards goals.
- Organisation: The term refers to two related competency areas: personal organisational skills (how someone plans, prioritises, and manages their work) and organisational alignment (how well they align their efforts with the organisation’s goals and processes).
- Efficiency: Efficiency describes how well an employee uses resources (time, tools, processes) to achieve results with minimal waste. It’s about productivity, time management, and process improvement.
In a typical 360 questionnaire, you will have multiple questions under each of these competency areas. A brief template structure with these topics can look like this:
- Communication: 3–5 questions (e.g., clarity, listening, adapting message).
- Teamwork/Interpersonal: 3–5 questions (e.g., collaboration, empathy, conflict resolution).
- Problem Solving/Decision Making: 3–5 questions (analysis, creativity, involvement, decisiveness).
- Leadership/Management: 3–5 questions (for those in leadership roles – vision, motivation, feedback, delegation).
- Organization & Efficiency: 3–5 questions (time management, priority, alignment with goals, process improvement).
- Open-ended questions: 2–3 prompts (e.g., “What is this person’s greatest strength?” and “What is one area for improvement?” and possibly “Any additional comments?”).

Post-Feedback Action Steps and Professional Development Plans
A 360-degree feedback exercise is truly valuable only if it leads to action and development. Elisa Di Mauro, Senior Manager of Talent Development at Rent the Runway, puts i t this way:
For the feedback to be successful, there needs to be a system for collecting and distributing it. There also needs to be guidance, success criteria, and examples of what good feedback sounds like. This framework can help people get more comfortable giving the feedback.
So, after you have written your 360 feedback questions, distributed them, collected the results and analysed the data, make sure to:
· Give the feedback recipient time to absorb the results
· Hold a debrief discussion (with manager, HR, or a coach)
· Develop a written action plan (Individual Development Plan)
· Follow up and demonstrate accountability
· Support with training and coaching
Why go through all of these steps?
Tanya Rice, CIPD’s HR project manager, explains it briefly:
The 360 programme has enabled us to have honest, and insightful conversations with our senior leaders, and raise their awareness of their impact. We have developed both tailored individual action plans, and incorporated common development needs into our senior leaders programme.
The testimonials from HR managers demonstrate that when post-feedback steps are done right, 360 feedback becomes a powerful catalyst for professional growth rather than just an assessment.
360-degree feedback questions are an excellent way to facilitate important conversations within your organisation. They can benefit both managers and leaders, as well as employees in understanding and improving their core competencies. More importantly, there are all sorts of tools at your disposal for analysing and making sense of the qualitative and quantitative data.
At Future Savvy, we offer instructor-led training programs that can help improve your data analysis skills and grow your business. Contact us today!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What’s the main takeaway for CIOs?
Treat AI as a product mandate: embed, govern, and scale it across priority journeys - not as side pilots.
High-volume service and operations, plus risk/AML and treasury forecasting embedded into existing platforms.
No - most impact comes from integrating AI into current digital channels, case tools, and workflows.
Use unified, curated data sources, retrieval grounding, human-in-the-loop controls, and monitoring/audit trails.
Related Articles
 L&D Insights
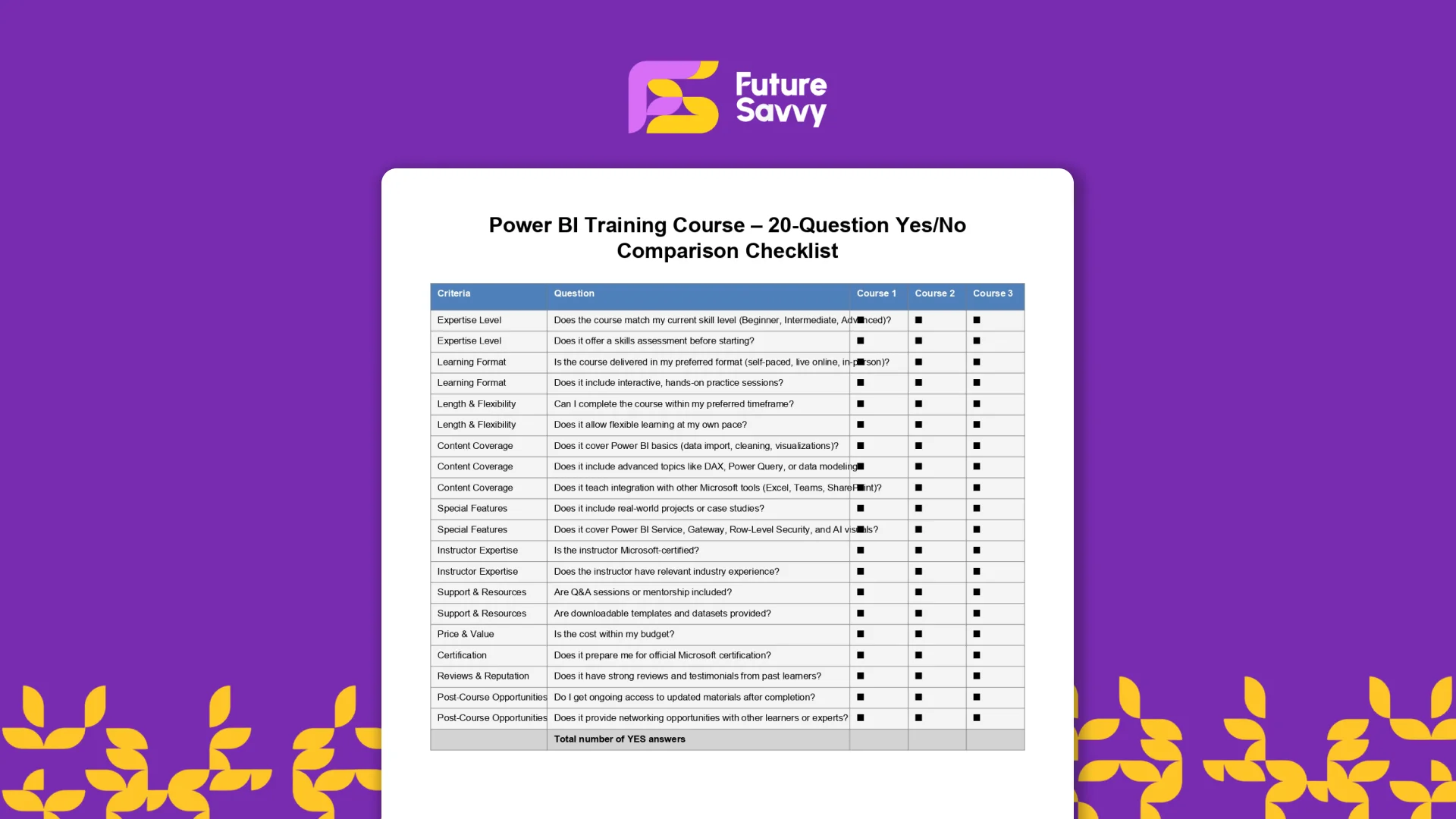
L&D InsightsPower BI Training Course – 20-Question Comparison Checklist
The Power BI Training Course – 20 Questions Checklist is a practical, printable tool to compare Power BI courses across providers objectively. Use it to score curriculum quality, delivery format, hands-on practice, certification prep, and after-course support so you can choose with confidence.
 L&D Insights
L&D InsightsBasic vs. Advanced SQL Training Courses: What is the difference?
The article explains what SQL training courses cover at basic and advanced levels, highlighting their shared focus on hands-on practice. It contrasts beginner courses that teach core querying and database concepts with advanced courses that tackle complex joins, window functions, CTEs, indexing, and performance. It outlines certifications, career paths, and why SQL remains a high-demand skill across roles like analysts, engineers, and developers. Finally, it offers criteria for choosing the right course and showcases instructor-led options from providers such as Future Savvy and others.
 L&D Insights
L&D InsightsLiteracy vs Digital Literacy: What Are the Differences?
Traditional reading-and-writing literacy has broadened into digital literacy—the ability to locate, evaluate, create, and communicate information safely and effectively through technology. The article traces this evolution from basic “computer literacy” of the 1990s to today’s multifaceted concept that spans information, media, and AI literacy. Digital skills now underpin social inclusion, workforce readiness, and democratic participation, while gaps in access, competence, and support exacerbate inequality.
