- TIPS & TRICKS/
- How to Use the Len Command in Excel/


How to Use the Len Command in Excel
- TIPS & TRICKS/
- How to Use the Len Command in Excel/
How to Use the Len Command in Excel
Excel has a variety of text functions that help you extract, combine, format, understand, and work with your text data in general. While TRIM, PROPER, LEFT, RIGHT, and other functions are more commonly used, the LEN function still has its place and is important to know how to use correctly.
This guide has a closer look at this function and helps you learn more about the LEN command in Excel, including what it is, how to use it, and common issues to watch out for while using it.
Want to learn morea bout Excel’s various functions? Make sure to check out our instructor-led Excel training courses!
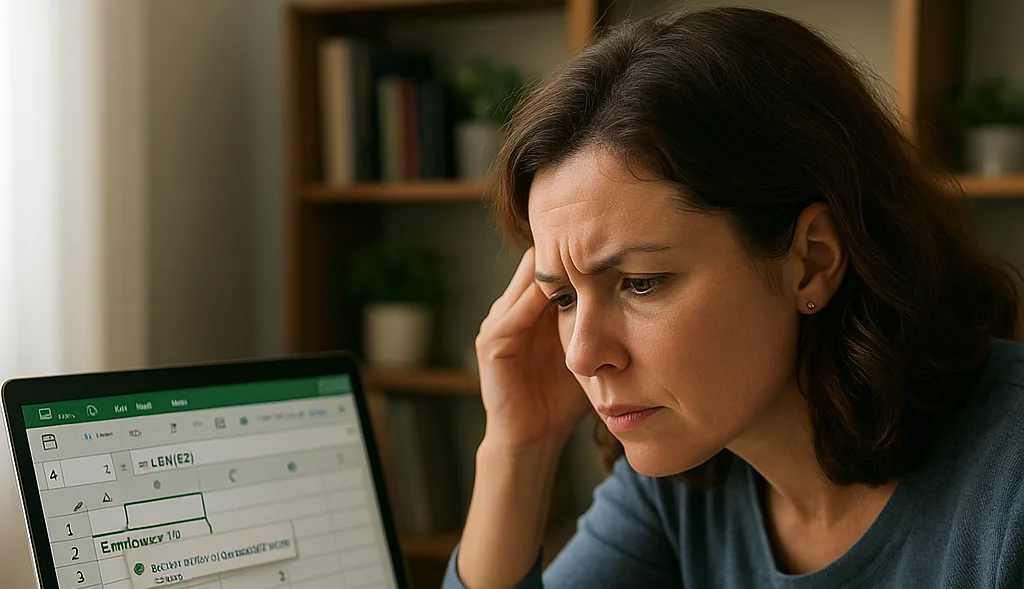
What Is the LEN Command in Excel?
The LEN command in Excel is a text function that returns the exact number of characters in a text string in a cell. In addition to letters, it also counts spaces, punctuation, and numbers. It’s easy to remember what LEN helps you do, as it’s the first three letters in the word “Length”.
It’s useful for validating data to ensure each cell contains the right number of characters, and it is also great for data cleaning, as it may help you identify cells with improper character counts, which may mean there are leading/trailing spaces or other issues with the data.
Understanding the Syntax of the LEN Function
The syntax of the LEN function is among the most basic and easy to understand in all of Excel, as it’s just =LEN(text). The LEN part of the syntax is telling Excel to count characters, and the “text” part tells Excel what word, string, or cell to count.
For example, if you include =LEN(“Excel”), your result is five, as there are five characters in the word “Excel”. But if you include =LEN(B2), then the result will be however many characters are in the text string of the “B2” cell.
Practical Examples of Using LEN in Excel
Now that you’re aware of how the LEN function works and what it does, let’s go over some examples of how and why you may use the LEN function in Excel.
Count Characters in a Single Cell
Counting characters in a single cell is straightforward and only takes a few steps. In this example, let’s say a company has 5-digit employee IDs for all of its staff, and wants to ensure none of the employee IDs are longer or shorter in its database by mistake.
1. Open your spreadsheet that contains your employee data.
2. Add a new column, which you may title as something like ‘Employee ID characters”.
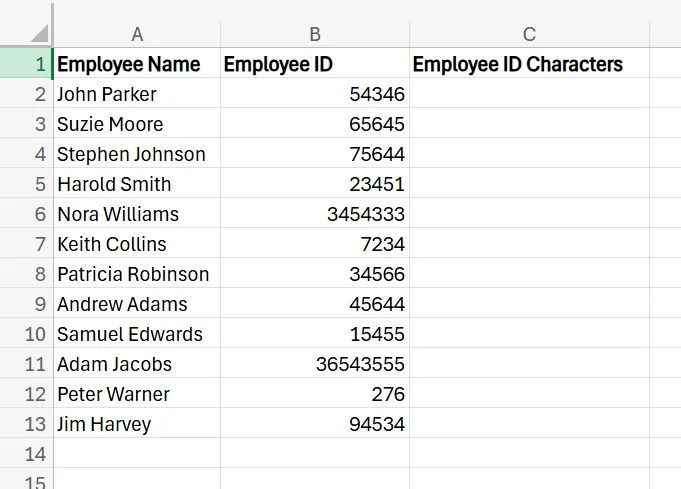
3. In the first row of that new column, enter =LEN(B2). Of course, use whichever cell it is in your specific scenario.
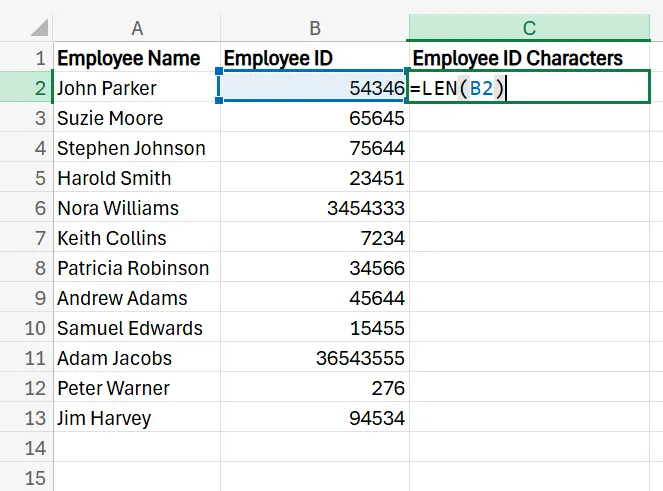
4. After pressing Enter, you’ll see the character count for that specific cell.
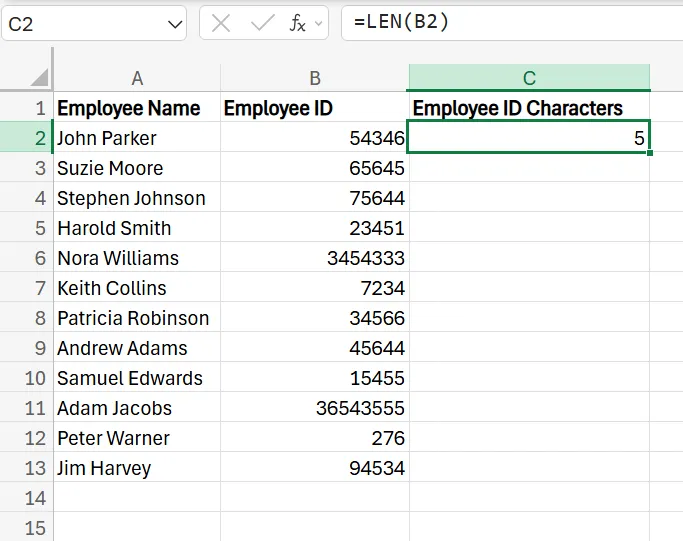
5. Drag the formula down to the rest of the rows to apply it and instantly see how many characters are in each cell.
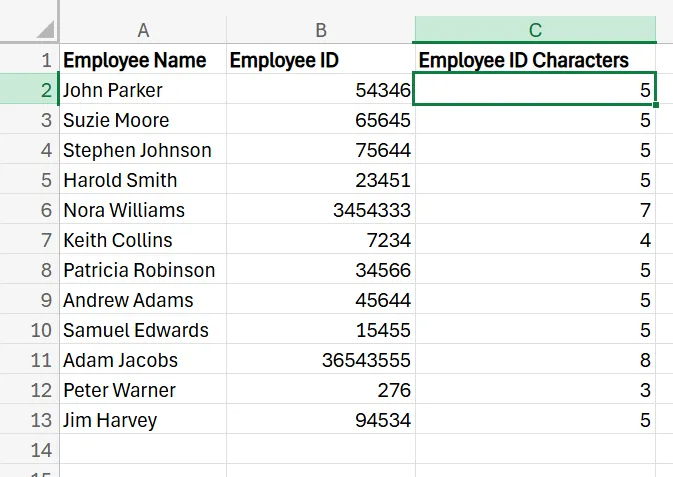
Now you can easily scroll through the results and check the IDs in the rows where the returned number is anything but five and make adjustments/corrections as needed.
Count Total Characters Across Several Cells
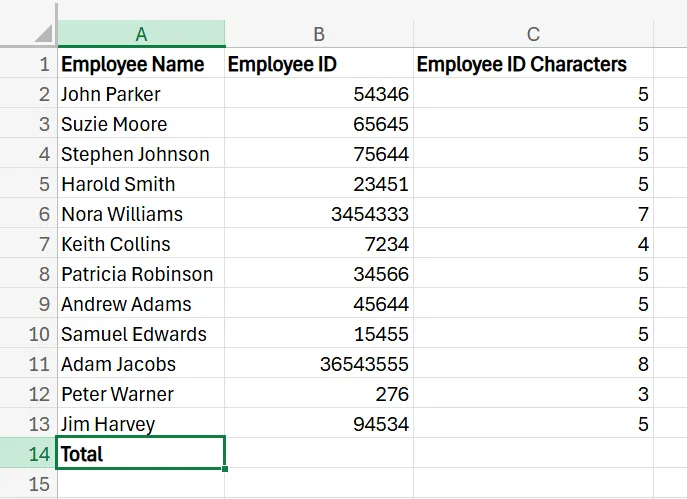
If you want to count the total characters across all of your cells, as opposed to one, you can easily accomplish this with LEN as well. Begin with the same employee data spreadsheet, and add a new row at the bottom of your results, called “Total”.
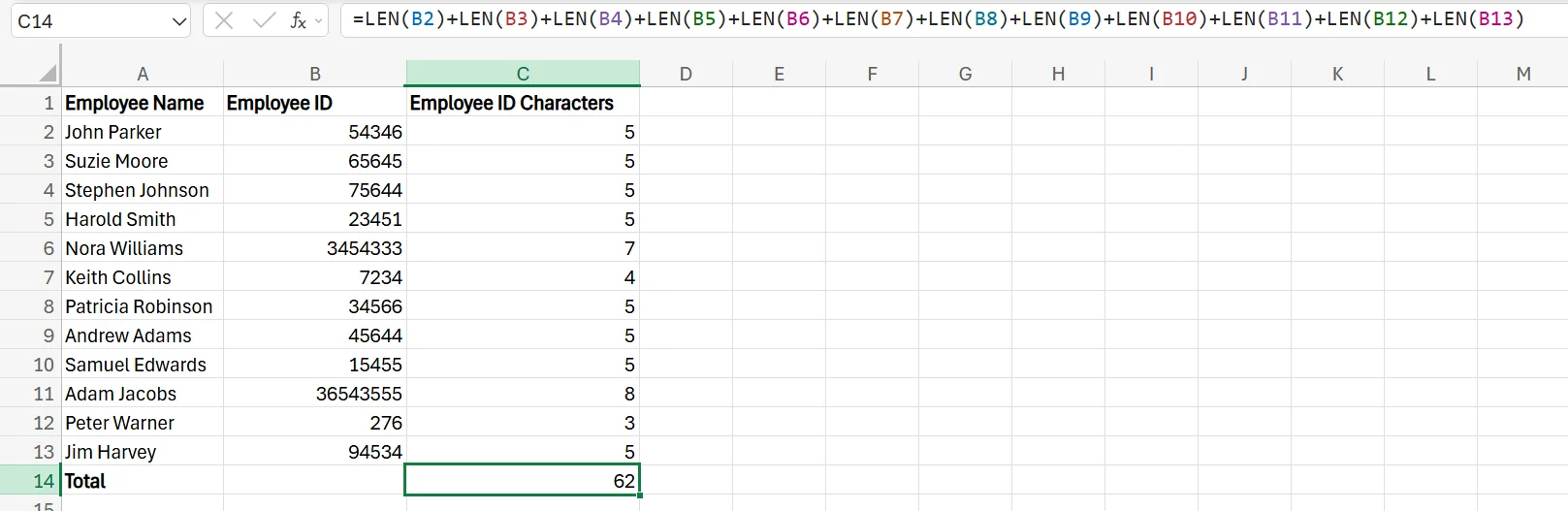
3. In the “Employee ID characters” cell of this row enter =LEN(B2)+LEN(B3)+LEN(B4)+LEN(B5)+LEN(B6)+LEN(B7)+LEN(B8)+LEN(B9)+LEN(B10)+LEN(B11)+LEN(B12)+LEN(B13) and hit Enter. This adds up all the characters of the employee IDs in total.
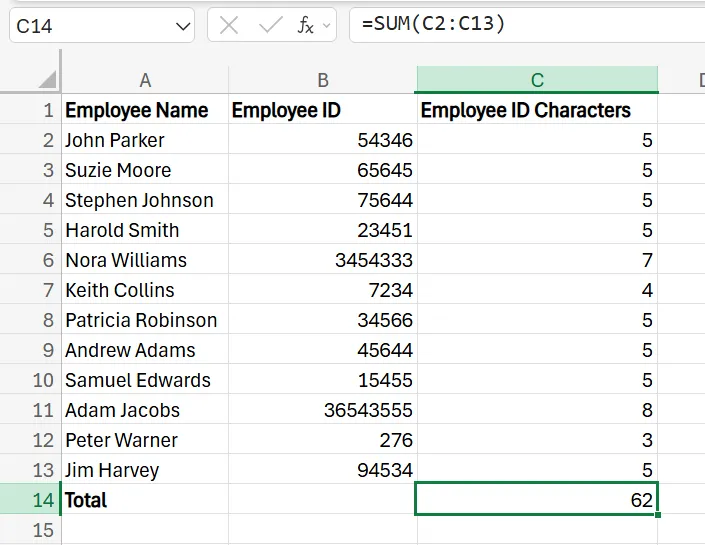
In addition to using the LEN formula to gather this total, you can also use the SUM function. Simply enter =SUM(C2:C13) and Excel adds up the total numbers of that range, giving you the total characters of all cells together.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with LEN
While the LEN function is among the simplest to use in Excel, there’s still a chance you may run into some issues with it. Here are a few common problems you may experience with the LEN function, as well as how you can deal with them.
Hidden Spaces
If your cells are full of hidden spaces (such as leading or trailing spaces), it may mess up the results of a LEN calculation. Even if you don’t see the leading or trailing spaces visually, Excel will calculate them, which may skew your results. The way to fix this is to use the TRIM function to remove any hidden spaces before running the LEN function.
Improper or Inconsistent Cell Formatting
If you have a database that includes a mix of numerical and text data, some LEN calculations may experience issues. For example, =LEN(23) gives you a result of two, whereas =LEN(“twenty three”) gives you a result of 12. Because of this, always ensure cells are in the right format before applying the LEN function to them.
Issues With the Formula/Syntax Itself
While the syntax for the LEN function is simple, it’s still possible to accidentally make a mistake. Maybe you missed a letter, forgot to add quotation marks around a word, or accidentally clicked on the wrong cell.
If your LEN commands aren’t working properly, despite your data being correct, it never hurts to check the formula and make sure nothing is out of place.
Get in touch with us today to discuss how we can help you grow your business!
Related Articles
 Tips & Tricks
Tips & Tricks Tips & Tricks
Tips & TricksHow to Compare Two Columns in Excel
This article explains how to easily compare two columns in Excel, especially when working with large datasets. It outlines common methods such as using formulas like IF, EXACT, and VLOOKUP, as well as conditional formatting to highlight differences or similarities. The guide also covers why column comparison is useful for identifying duplicates, missing values, and patterns in data. Finally, it offers best practices like ensuring data compatibility, verifying formulas, and labelling columns clearly for accuracy.
 Tips & Tricks
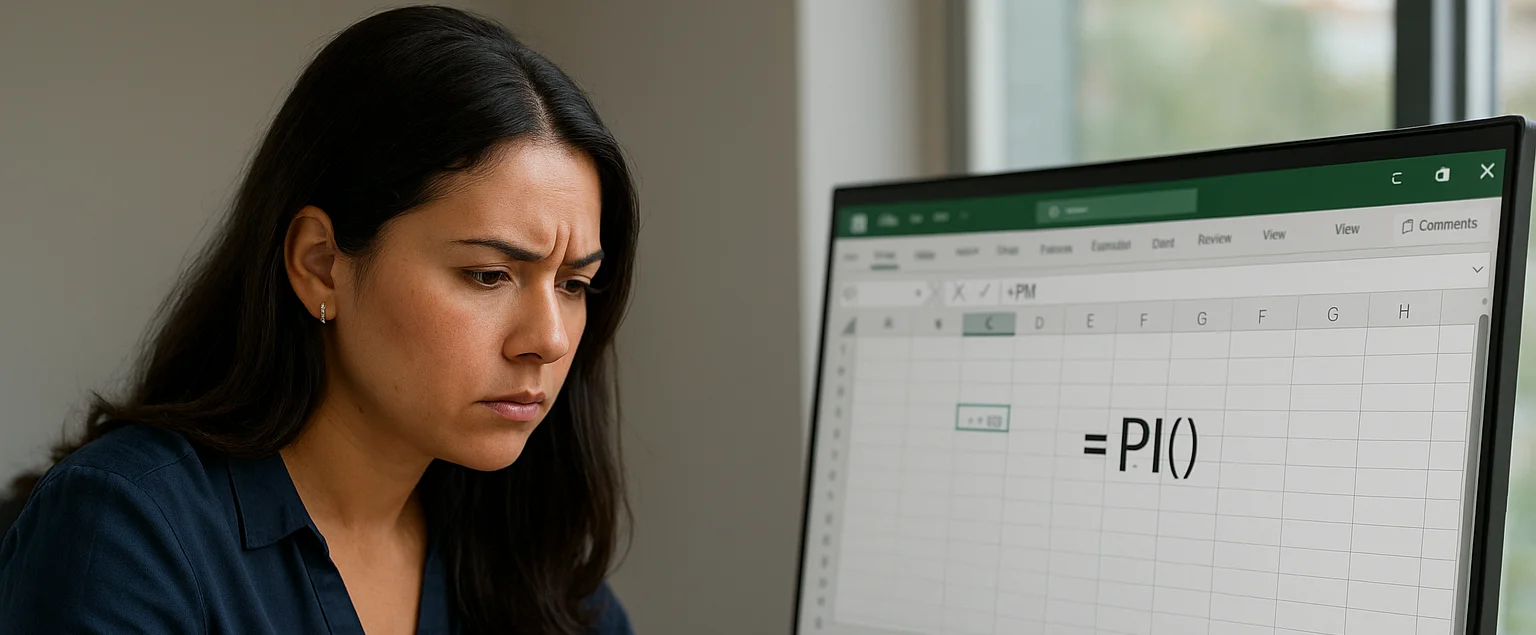
Tips & TricksHow to Use Pi in Excel
Pi (π), the irrational constant ~3.14159 that underpins circular and spherical calculations, is crucial for geometry, trigonometry, and many real-world tasks. In Excel you can insert π with the
=PI()function, adjust its decimals, add the π symbol, and embed it in formulas. For example,=PI()*r^2to find a circle’s area. These techniques power advanced analytics in finance, engineering, architecture, fluid dynamics, and other business scenarios where precise circular measurements matter.
